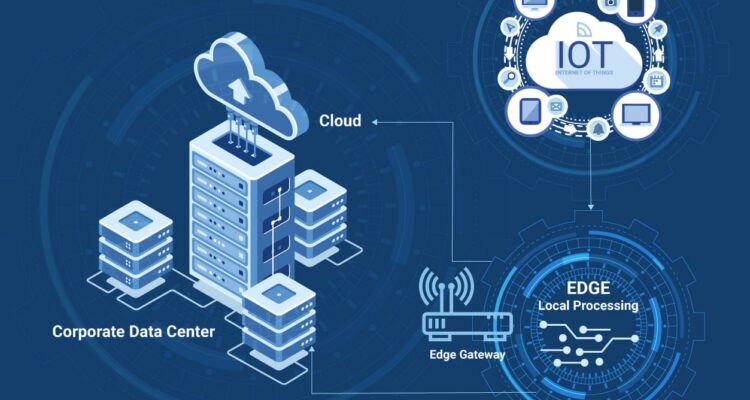
Edge computing for IoT devices allows businesses to store data closer to the edge rather than sharing it with data centers or the cloud that are physically distant.
With the use of edge computing, it is critical to reducing the major obstacles that IoT devices encounter. Enhanced security and faster data transfer are two of the benefits.
The world is rapidly heading toward an IoT-driven future, but it is not without its own set of challenges, which pose a serious threat to both businesses and consumers. User data privacy, bandwidth costs, latency, and a long data processing time are all key concerns. By implementing edge computing for IoT networks, this can be mitigated, if not totally eliminated. It is critical to developing a better framework to overcome cloud computing’s disadvantages for IoT devices in order to demonstrate its efficacy in the IoT structure.
The IoT framework is facing increased hurdles as a result of the enormous number of devices connected to the internet. And there are dangers to be aware of:
- Data Privacy: IoT devices collect massive volumes of important user data, which raises privacy concerns. If data is not handled properly or if security measures are not in place, it can be exploited. This has a significant detrimental influence on a company’s brand identity and other financial prospects. Cybercriminals can destroy IoT devices and render them useless to users, making data sharing with complex user connections a huge problem for businesses.
- Attacks by botnets: Because the IoT architecture is entirely reliant on devices being linked to the internet, all IoT devices are extremely vulnerable to cyber-attacks. Botnets can be used by cybercriminals to infect devices and networks. DDoS attacks are the most common source of botnet attacks.
- Costs are really high: Data storage costs a lot of money for organizations to process and store data through the network, and server upkeep adds to the company’s operating costs. Data storage is generally outsourced to third-party companies, which drives up expenses dramatically. This can be costly for SMEs, emphasizing the need for a cost-effective solution.
- High Latency and Low Responsiveness: IoT devices are capable of receiving and transmitting data at extremely high speeds with no latent loss. If IoT devices experience connectivity problems, they may become slow or unresponsive in processing user requests. High latency causes delays, which can become aggravating and lead to financial losses for enterprises. If an IoT device experiences undesirable latency, its usefulness is reduced, and it becomes a liability rather than an asset.
How Edge Computing Helps to Solve These Problems
Edge computing helps IoT networks overcome substantial dangers by enabling them to have high responsiveness and low latency. With edge computing, the data centers are closer to the endpoints. As data transfers between a decentralized and distributed data system, there is a considerable gain in device responsiveness and a reduction in latency. As a result, the network’s bandwidth is increased, ensuring a quick data flow.
Because IoT systems rely on high-speed data transmission, edge computing can greatly improve performance. It provides advanced security for IoT devices while also delivering enhanced computational capability at lower rates.
Edge computing has the potential to change the way IoT devices collect, store, access, and analyze data. It can also vastly improve the way IoT devices communicate and interact with one another. Edge computing for IoT, when paired with other technologies like artificial intelligence, 5G, and machine learning, can propel us quickly toward a safe, fast, and dependable IoT future.
The issues that IoT devices confront can be significantly eased by increasing data transfer speeds between devices and ensuring user data privacy. Businesses and consumers alike can gain a lot from adding cutting-edge technology like edge computing into their IoT architecture.
Like this post? Checkout our Featured Stories Section