Many businesses are combining internet-of-things (IoT) technology to improve operational processes, expand digital capabilities, and separate products and services.
However, as businesses implement a diverse range of IoT projects and use cases, each with its own set of requirements, many are having difficulty implementing centralized cloud-based and data center analytic techniques.
Enterprises must reassess their IoT strategies, architecture, and skills in order to transform huge quantities of IoT data into insights in a secure, rapid, and cost-effective manner.
Edge IoT Analytics is gaining traction in this area.
What are the Benefits of Edge IoT Analytics?
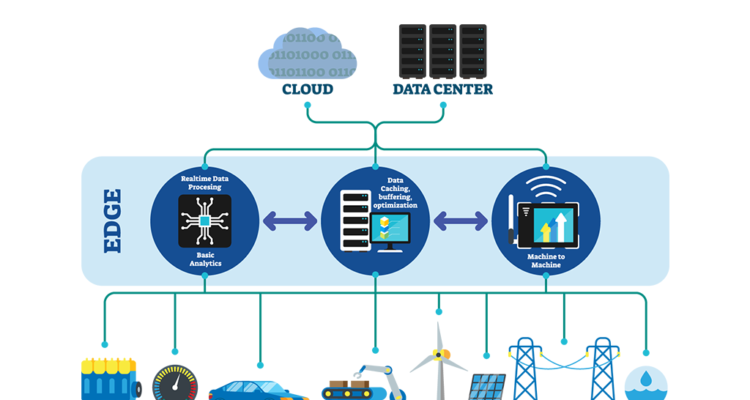
Edge IoT Analytics is a method of moving analytic computations for specific IoT use cases out of the data center or cloud and placing them as close to the data sources as possible to reduce security and compliance risks, enable real-time choices, and lower costs.
Incorporating Edge IoT analytics can help firms overcome the limits of a fully centralized analytics approach.
The fact that the “edge” as we know it is getting increasingly intelligent is one of the main reasons why the edge has grown so popular in today’s digital world.
Computing at the edge that is intelligent IoT analytics usually has more powerful processing capabilities that are designed to look at data at the edge.
According to IoT Analytics’ newest research on Industrial IoT edge computing, intelligent edge computes resources are rapidly replacing “dumb” older edge compute resources. While intelligent edge computing currently accounts for a small percentage of the industry, it is predicted to develop at a considerably quicker rate than the total market, allowing it to gain market share. The edge computing propaganda is important because the transition from “dumb” edge computing to “intelligent” edge computing has enormous implications for enterprises across the board, from manufacturing to consumer electronics to oil and gas wells to machinery OEMs.
Many firms have used cloud platforms to evaluate their IoT data by utilizing cloud platforms’ substantial processing power, connection, and storage capabilities, as well as cutting-edge analytics models.
However, they have identified cloud analytics limitations that are particularly important for effective IoT use case adoption, such as a lack of real-time analytic capabilities, security or compliance problems, and high data transmission costs.
Businesses have challenges when analyzing IoT data in the cloud.
To combine rich device data with low-cost, adaptable global infrastructure, many businesses have switched to cloud platforms.
Initially, this strategy allowed companies to accelerate the development of linked devices and industrial internet solutions.
However, when businesses ramp up their IoT initiatives, totally centralized or cloud-only models are likely to falter.
When adopting cloud computing platforms, intensive IoT applications for data and task loads face problems. The biggest drawbacks of evaluating IoT data in the cloud include limited accessibility and the inability to make real-time choices, as well as security concerns and rising costs.
Because IoT use cases typically have unique real-time data analysis requirements, moving, storing, and analyzing IoT data into a core cloud infrastructure is not necessarily cost-effective, practicable, or even legal.
While IoT data analysis in the cloud has limitations as it grows in popularity, organizations are using it as a strong source of insight.
IoT data is being used by businesses as a valuable source of information.
Enterprises may now acquire an unprecedented amount of IoT data because of the proliferation of networked IoT devices and constant innovation.
Data and insights have become valuable assets for any business, with data-driven decision-making governing every part of our life.
The value of this data is determined by how businesses analyze and interpret it in order to achieve better results.
While businesses are embracing IoT data as a valuable source of information, dealing with data, analytics, and security challenges remains a struggle.
Managing IoT data presents a number of challenges.
Some of the major IoT data analysis roadblocks are a lack of analytical capabilities, security issues, and real-time data analysis issues.
The problem will be figuring out how to handle and store all of that information. Time series database management systems, event stream processing platforms, and specific analytical algorithms are sometimes needed to organize and store this data in an efficient and timely manner. Many BI and analytics professionals, on the other hand, are unfamiliar with streaming analytics, time-series data management, and other IoT analytics technologies.
Despite these obstacles, Intelligent Edge IoT Analytics has shown to be a game-changer for many businesses, bringing several business and operational benefits.
Businesses that implemented edge IoT analytics saw cost savings, greater real-time decision making, improved business processes, privacy preservation, expanded security capabilities, and a better customer experience, to name a few.
The following are some key recommendations gained from credible study reports:
- To recognize IoT use cases and architecture requirements, simplify synchronization between IT and operations.
- Recognize IoT use cases that meet your company’s current and future business transformation objectives.
- Consider your requirements for IoT data analytics at the edge.
- To accelerate your edge IoT projects, seek assistance from partners.
Many IoT decision-makers think that promoting Edge IoT Analytics can improve IoT outcomes.
Final Thoughts
Switching to contemporary, intelligent edge computing architectures may save a lot of money and open up new options for businesses that manage physical assets.
For more blogs checkout: Blogs